Understanding MMDA Traffic Rules and Regulations in the Philippines
Living in a bustling metropolitan city like Manila can be both exciting and challenging. One of the biggest challenges we face on a daily basis is dealing with traffic. To help manage the flow of vehicles and ensure road safety, the Metropolitan Manila Development Authority (MMDA) has implemented various traffic rules and regulations. In this article, we will explore some of the key MMDA traffic rules and regulations in the Philippines.
1. Number Coding Scheme
The Number Coding Scheme, also known as the Unified Vehicular Volume Reduction Program (UVVRP), is one of the most well-known traffic regulations in Metro Manila. Under this scheme, vehicles are prohibited from plying the roads on certain days based on the last digit of their license plate number. This rule aims to reduce traffic congestion and encourage carpooling or the use of public transportation.
2. Yellow Lane Policy
The MMDA implements the Yellow Lane Policy to ensure the smooth flow of traffic along major roads. The yellow lane is designated for public utility vehicles (PUVs) such as buses, jeepneys, and taxis. Private vehicles are not allowed to enter or use the yellow lane, except when making a right turn or overtaking a slower vehicle.
3. Motorcycle Lane Policy
In an effort to address the increasing number of motorcycle-related accidents, the MMDA has implemented the Motorcycle Lane Policy. Motorcycles are required to stay within the designated motorcycle lane, which is usually located on the rightmost side of the road. This regulation aims to separate motorcycles from other vehicles and reduce the risk of accidents.
4. No Contact Apprehension Policy
The MMDA has introduced the No Contact Apprehension Policy to catch traffic violators without the need for physical apprehension. Through the use of CCTV cameras and other surveillance technologies, the MMDA is able to monitor and record traffic violations. Violators are then sent a citation ticket by mail, which includes the details of the violation and the corresponding penalty.
5. Anti-Distracted Driving Act
The Anti-Distracted Driving Act prohibits the use of mobile devices while driving unless used in hands-free mode or for emergency purposes. This law aims to reduce accidents caused by distracted driving, which includes texting, calling, browsing the internet, or watching videos while operating a vehicle.
6. Road Clearing Operations
The MMDA conducts regular road clearing operations to remove obstructions on public roads. These obstructions include illegally parked vehicles, sidewalk vendors, and other structures that impede the flow of traffic. By clearing the roads, the MMDA aims to ensure the safety and convenience of motorists and pedestrians.
7. Speed Limit Enforcement
Speed limits are enforced by the MMDA to promote road safety and reduce the risk of accidents. The maximum speed limit on major roads in Metro Manila is 60 kilometers per hour (kph), while the limit on residential areas is 30 kph. It is important for drivers to adhere to these speed limits to prevent accidents and maintain orderly traffic flow.
These are just some of the key MMDA traffic rules and regulations in the Philippines. It is important for motorists to familiarize themselves with these rules to avoid penalties and contribute to the overall improvement of traffic conditions in Metro Manila. Remember, by following these regulations, we can all work towards a safer and more efficient road system in our beloved city.
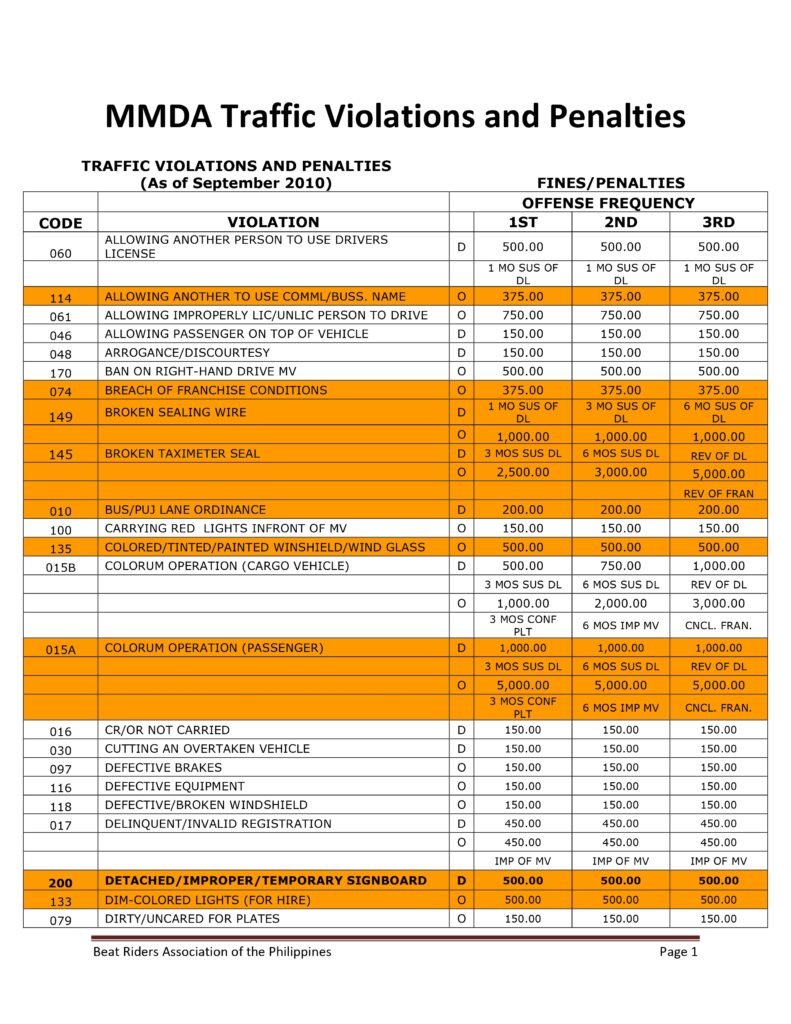
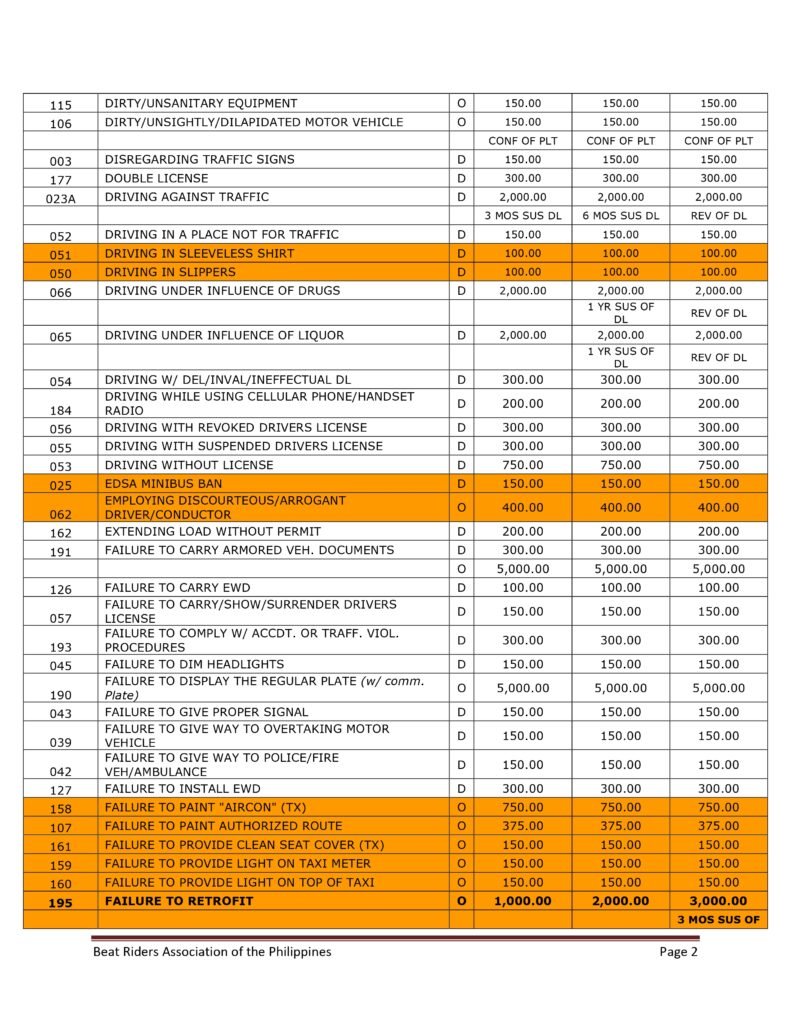
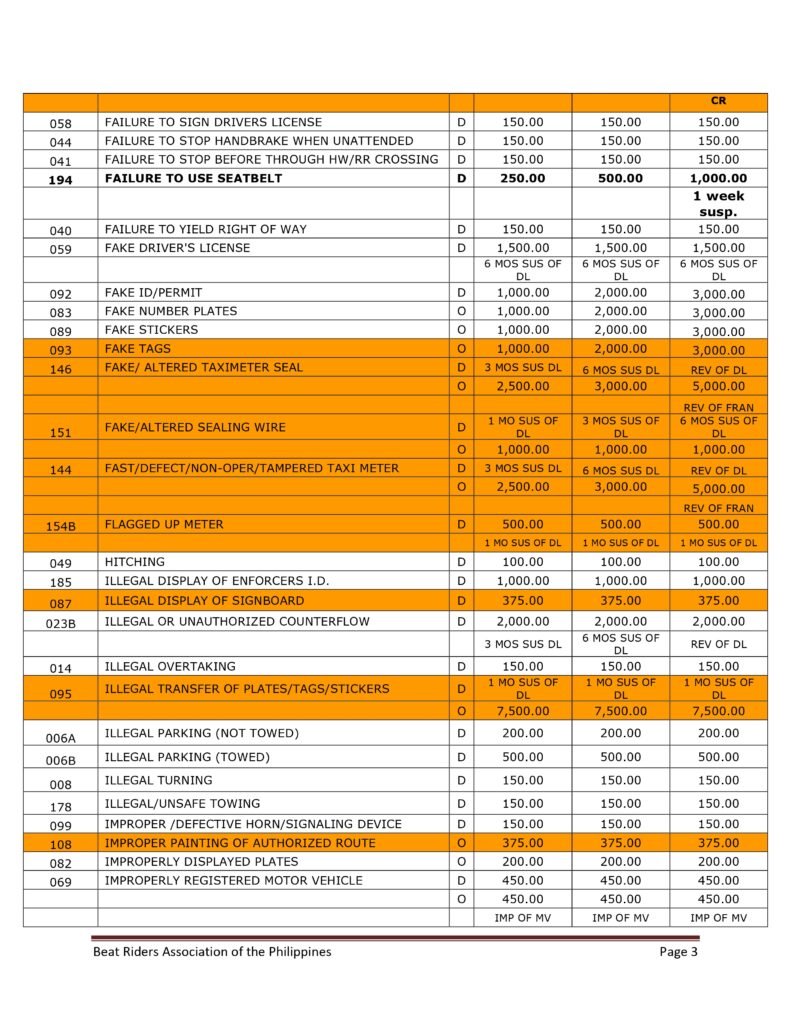
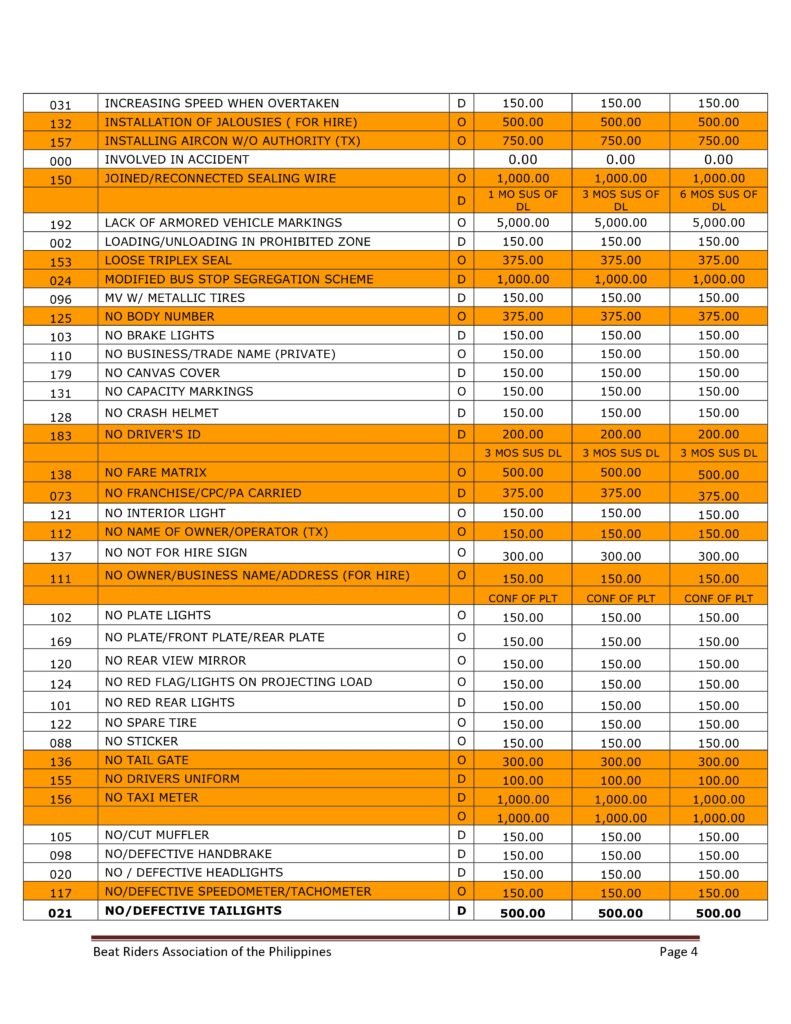
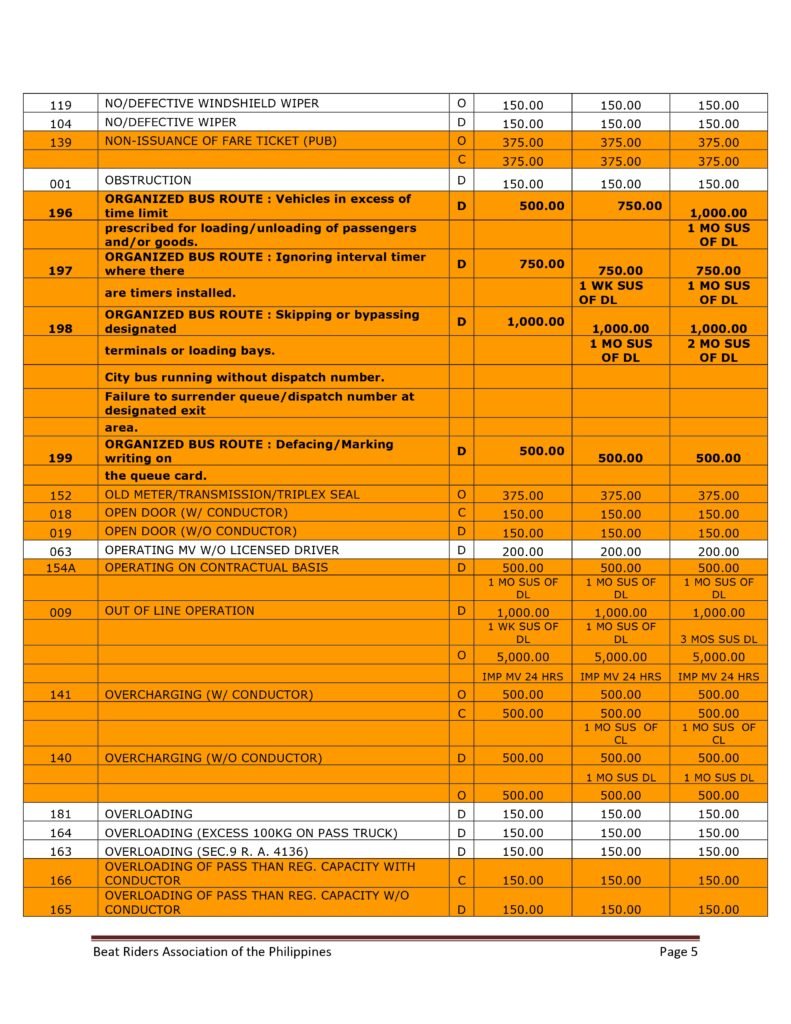
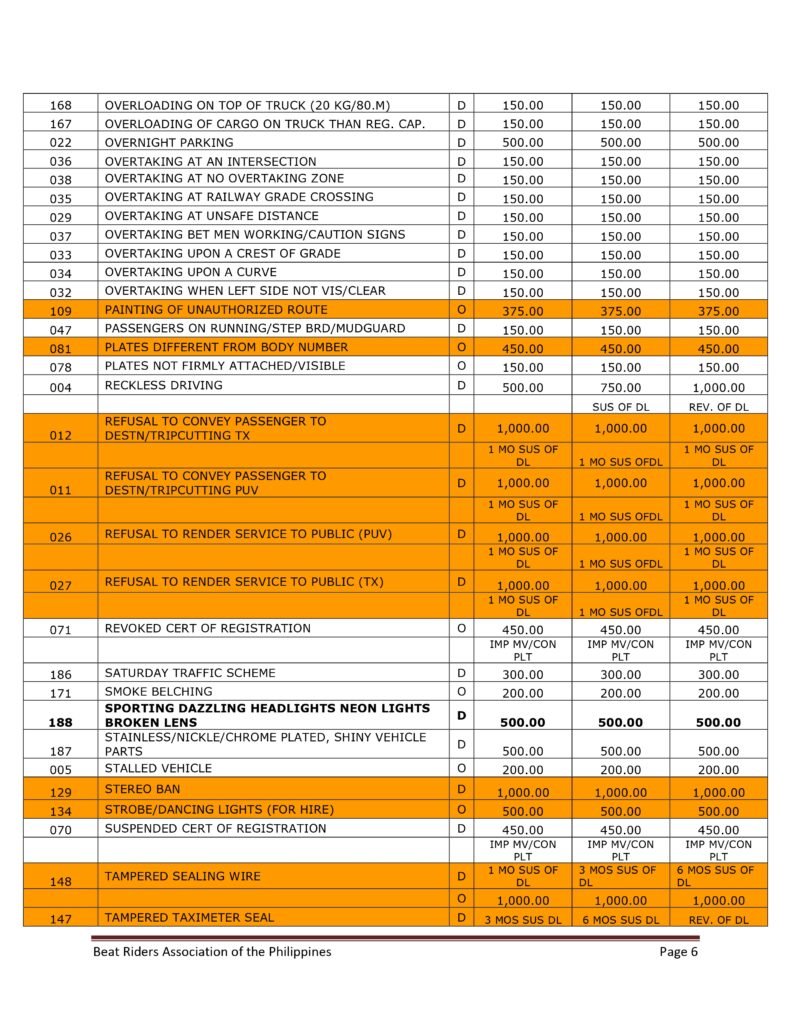
MMDA Traffic Violations and Penalties Tariffs